Transthoracic Echocardiography
Echo, is a painless test that uses sound waves to create moving pictures of your heart. The pictures show the size and shape of your heart. They also show how well your heart’s chambers and valves are working. Echo also can pinpoint areas of heart muscle that aren’t contracting well because of poor blood flow or injury from a previous heart attack. A type of echo called Doppler ultrasound shows how well blood flows through your heart’s chambers and valves. Echo can detect possible blood clots inside the heart, fluid buildup in the pericardium (the sac around the heart), and problems with the aorta. The aorta is the main artery that carries oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your body.
Risks:
No risks involved. Patients may at times experience minor soreness around the ribs.
Preparation:
- Fasting not required
- Do not need anything specific preparation prior this test
- Continue all medications
What to expect:
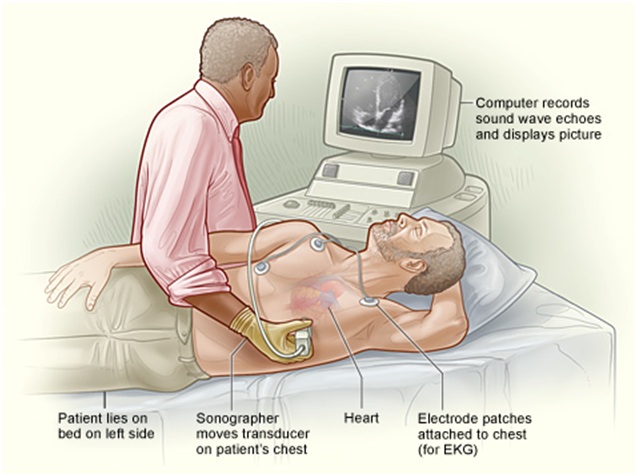
- For most types of echo, you will remove your clothing from the waist up. Women will be given a gown to wear during the test. You’ll lie on your back or left side on an exam table or stretcher.
- Soft, sticky patches called electrodes will be attached to your chest to allow an ECG (elec trocardiogram) to be done.
- A doctor or sonographer (a person specially trained to do ultrasounds) will apply gel to your chest. The gel helps the sound waves reach your heart. A wand-like device called a transducer will then be moved around on your chest.
- The transducer transmits ultrasound waves into your chest. A computer will convert echoes from the sound waves into pictures of your heart on a screen.
- During the test, the lights in the room will be dimmed so the computer screen is easier to see. activity.
A report will be sent to your referring doctor, usually within 24 hours. Your doctor will discuss your results at your next appointment. If you require your report sooner please inform either the reception staff or the technician.
